Accounting for Liabilities
This adds to the complexity of lease amortization and calculation of the discount rate. This article illustrates how to account for this type of transaction by discussing several important accounting issues, including the derivation of the effective interest rate. This article examines two cases involving bonds and leases and provides a complete guide on how to calculate the effective rate using Excel Goal Seek and develop the amortization schedule. The gap between the two methods of valuation is significant as regards long term liabilities. In a QuickBooks sense, a liability is a creditor’s claim on a company’ assets. In other words, the creditor has the right to confiscate assets from a company if the company doesn’t pay it debts.

Comparing Current and Non-Current Liabilities
Liabilities in accounting are grouped based on how soon they need to be repaid. Next, let’s explore the different types of liabilities and how they are categorised. You will be eligible for a full refund until two weeks after your payment date, or (for courses that have just launched) until two weeks after the first session of the course begins, whichever is later. You cannot receive a refund once you’ve earned a Course Certificate, even if you complete the course within the two-week refund period. IE Business School is an internationally recognized business school where the leaders of tomorrow shape their ideas and learn to become global citizens.

( Required Future Sacrifice of Assets:
- Managing accounts payable well helps maintain good vendor relationships and avoids late fees.
- Credit cards often have some of the highest annual percentage rates (APRs), sometimes above 20%.
- Liabilities are classified into three categories – current, non-current, and contingent.
- When you borrow money, record the liability by recognizing the amount you owe.
- The estimated cost of fulfilling these warranties is a contingent liability.
- Long-term notes payable are formal loan agreements with repayment terms exceeding one year.
These are not recorded on the balance sheet but are disclosed in the financial statement notes. Examples include pending lawsuits, product warranties, and environmental cleanup costs. The recognition of contingent liabilities depends on the likelihood of the event occurring and the ability to estimate the obligation’s amount. For instance, if a company is facing a lawsuit with a probable and estimable loss, it must disclose this information to provide accounting for liabilities a complete picture of potential financial risks.
Importance of Liabilities for Small Businesses
Short-term liabilities, also known as current liabilities, are obligations that are typically due within a year. On the other hand, long-term liabilities, or non-current liabilities, extend beyond a year. Besides these two primary categories, contingent liabilities and other specific cases may also exist, further adding complexity to accounting practices.
Liabilities in Accounting: Understanding Key Concepts and Applications
- These may be short-term or long-term, depending on the terms of the loan or bond.
- These current assets must also be converted to cash in time to pay the company’s obligations when they come due.
- Understanding these long-term commitments is important for evaluating a company’s financial leverage and its capacity for future investments.
- Liquidity refers to your business’s ability to meet short-term obligations.
These stem from past transactions and represent commitments the business must settle in the future, often through cash, goods, or services. Managing business finances is a complex and critical responsibility. https://rajubirion.com/2021/09/20/accounting-firm-sao-paulo/ Properly managing liabilities is essential for ensuring financial stability and supporting long-term growth. In conclusion, liabilities play a crucial role in business operations, as they represent the financial obligations a company has to its employees, suppliers, lenders, and other stakeholders.
- Liabilities can include future services owed, short-term or long-term loans, or unsettled obligations from past transactions.
- The credit balance in this account comes from the entry wherein Bad Debts Expense is debited.
- Liabilities are an operational standard in financial accounting, as most businesses operate with some level of debt.
- When there is a transaction that creates obligation for the company to make future payments, a liability arises and is recognised as when goods are bought on credit.
- Solvency is your ability to meet long-term obligations and remain financially stable over time.
- This approach can be particularly useful in volatile markets, where the value of liabilities may fluctuate significantly over time.
- Common examples include accounts payable, which are amounts owed to suppliers, and accrued expenses, such as salaries or utilities that have been incurred but not yet paid.
What Does Liability Mean?
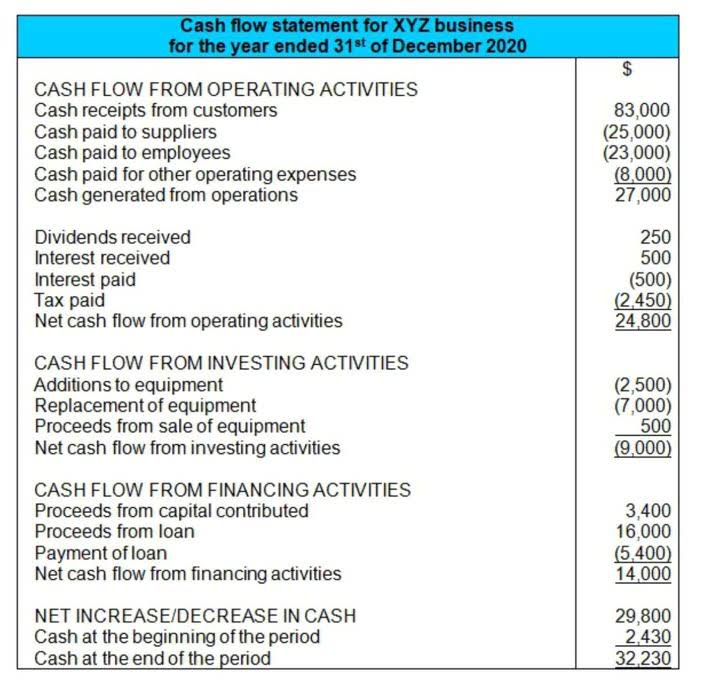
A well-managed operating cycle ensures that there is sufficient cash flow to meet these liabilities as they come due. A liability is something that a person or company owes, usually a sum of money. Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. They’re recorded on the right side of the balance sheet and include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses. In the statement of cash flows, liabilities can be reflected in several sections.
Liabilities should be recorded, as stated earlier, when an obligation occurs. Most liabilities presently included in financial statements qualify as liabilities because they require an enterprise to sacrifice assets in future. Thus, accounts and bills payable, wages and salary payable, long term debt, interest and dividends payable, and similar requirements to pay cash apparently qualify as liabilities. Once recognized, liabilities must be measured and reported at their appropriate values.

